Contents
Protection of Personal Data on the Internet

People use the Internet daily to work, socialize, shop, and study, constantly sharing information about themselves. For instance, they might provide bank card details while shopping online, include their phone number in a job application, or share their date and place of birth on social media.
Personal information is stored across numerous websites and applications, creating a risk of it falling into the hands of fraudsters. In this article, we will explain what personal data is, what it includes, how to protect it, and the dangers of data breaches.
What Is Personal Data?
Personal data is information that can identify an individual. This includes:
Full name, date, and place of birth
Passport details
Residential address
Phone number
Email address
Bank account information
Personal photos
Income level
Other information that relates to personal identification
Personal data cannot be used without the owner's consent. Thus, all services collecting such data must obtain permission and comply with security measures as personal data operators.
What Personal Data Do Websites and Applications Collect and Why?
Online services collect vast amounts of information. Users provide some data directly, such as when filling out registration forms or placing orders in online stores. This includes contact details, payment information, age, education level, and delivery addresses.
Another source is cookies, which are digital footprints that record actions performed on a website. For example, cookies can remind an online store of the items you viewed or added to your cart during a previous visit.
Processing personal data enables websites to create user profiles, identifying details such as gender, age, interests, country of residence, and income level. This information helps them show relevant ads, create personalized discounts, and recommend products or content.
While personalization can be convenient, leaving too much personal information online increases the risk of it falling into the wrong hands.
What Are the Dangers of Identity Theft?
Bank card fraud: Attackers target card details like numbers, expiration dates, and CVV codes to steal money. Although online services aim to protect payment information, they are not immune to attacks.
Document misuse: Fraudsters can use official documents such as passports or social security numbers to take out loans in your name.
Account hijacking: Criminals can access your social media or messager accounts using stolen phone numbers, usernames, or passwords to spread spam or send false requests for help.
To minimize risks, monitor the data you share online and take steps to protect it. For more on common fraud schemes, see our article, Information Security for Beginners.
How to Protect Personal Data
Fraudsters often exploit weak security points to steal personal data. Following basic internet security rules can significantly reduce this risk:
1. Use strong passwords. Create long, complex passwords with random characters. Logical patterns like names or birthdates are hard to avoid for humans, but such passwords are easy to guess. Better use a password generator and store passwords securely in an encrypted password manager.
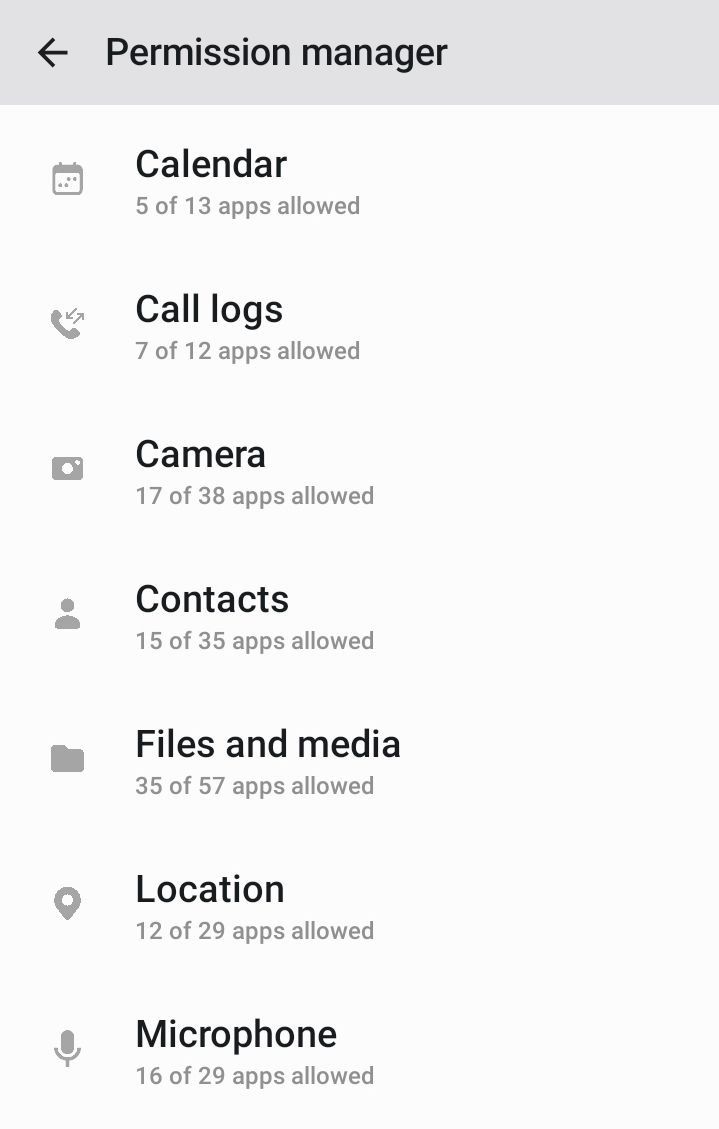
2. Check permissions. Websites and apps often request access to your data or device functions. For example, a messenger needs access to a camera for a video call. If the request looks strange and has nothing to do with the application's operation, it is better to refuse. Regularly review and disable unnecessary permissions in your device or browser settings under "Privacy" or "Permissions."
3. Enable two-factor authentication (2FA). Add an extra layer of security by requiring a second verification step (e.g., SMS code, email code, or fingerprint) alongside your password. Even if a password is compromised, this prevents unauthorized access.
4. Purchase a VPN. It encrypts traffic and hides your location, offering extra protection for personal data. Give preference to reliable service. For example, our BlancVPN received a score of 4.6/5 on Trustpilot. We do not store information about user actions and use only physical servers without virtualization, which excludes third-party access to information. It is especially important to enable a VPN when making financial transactions on the Internet and when using public Wi-Fi. Learn more: What Is a VPN and How It Works.
5. Install antivirus software. Antivirus programs warn you about fraudulent websites and block malware that could steal your personal data.
6. Avoid suspicious websites. Don't open attachments or follow links from suspicious emails. Ensure websites are secure by checking for "HTTPS" or a lock icon in the address bar.
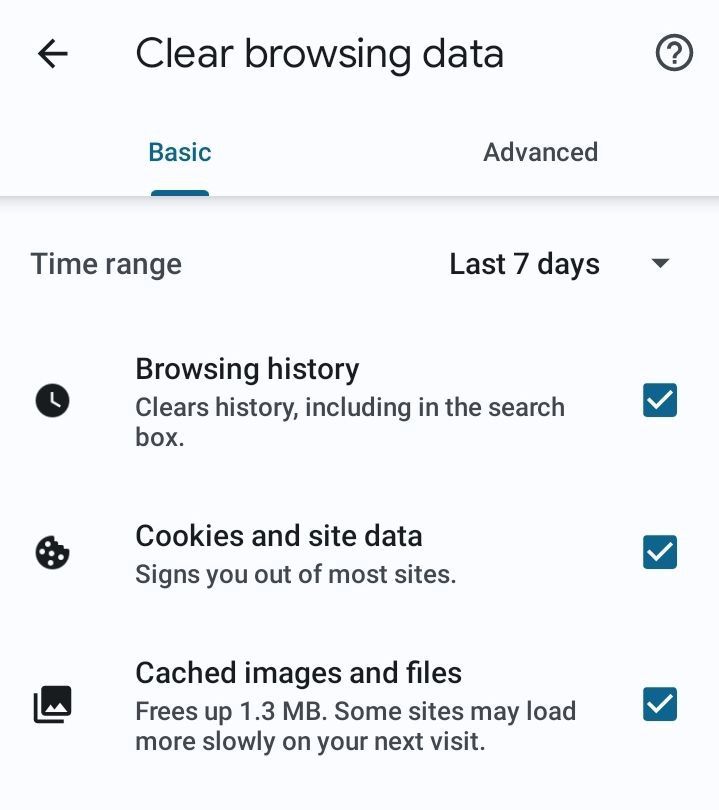
7. Clear cookies in browser settings from time to time. This will cause your logging out on most websites, but it's better to fill out the information again than to let scammers steal your data.
8. Update software regularly. Developers release updates to patch vulnerabilities and protect against new threats. Keeping your apps and operating system up to date minimizes risks.
9. Use a separate email address for online store registrations. This helps protect your main email account from spam and potential breaches.
10. Secure messenger data. Messengers can expose a wealth of personal information. In another article, we share tips on enhancing data security in Telegram, such as hiding your phone number, restricting calls, and reducing spam.
Remember that protecting personal data is an ongoing process requiring consistent adherence to security practices. While it demands effort, the reduction in fraud risk makes it worthwhile.
FAQ
What is personal data?
Personal data is the information that identifies a person, such as their full name, phone number, address, passport details, bank card information, and personal photos.
Why is protecting personal data important?
Scammers can use it to:
Steal money from your bank accounts.
Take out loans in your name.
Hack social media or messenger accounts.
How can I protect personal data online?
Use strong passwords.
Regularly check and manage app and site permissions.
Enable two-factor authentication.
Use a reliable VPN.
Install antivirus software.
Update software frequently.
Avoid suspicious websites and links.
Clear browser cookies regularly.
Use a dedicated email for online registrations.
Enhance messenger security settings.
BlancVPN — your gateway to safe and secure internet
Stream, browse, or work safely — even on public Wi-Fi.
Get BlancVPN